Arthritis is a term commonly used to describe joint inflammation, but it encompasses more than 100 different types of joint diseases. Among the most prevalent are Osteoarthritis (OA) and Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA). Although both conditions affect the joints and share some symptoms, they are fundamentally different in terms of cause, progression, and treatment. Understanding these differences is crucial for proper diagnosis, management, and improving quality of life.
Carticlas tablets are a cutting-edge dietary supplement formulated to promote joint health, reduce inflammation, and support overall well-being. They are designed to address the common issues associated with aging, high physical activity, and other factors that affect joint and bone health.
What is Osteoarthritis (OA)?
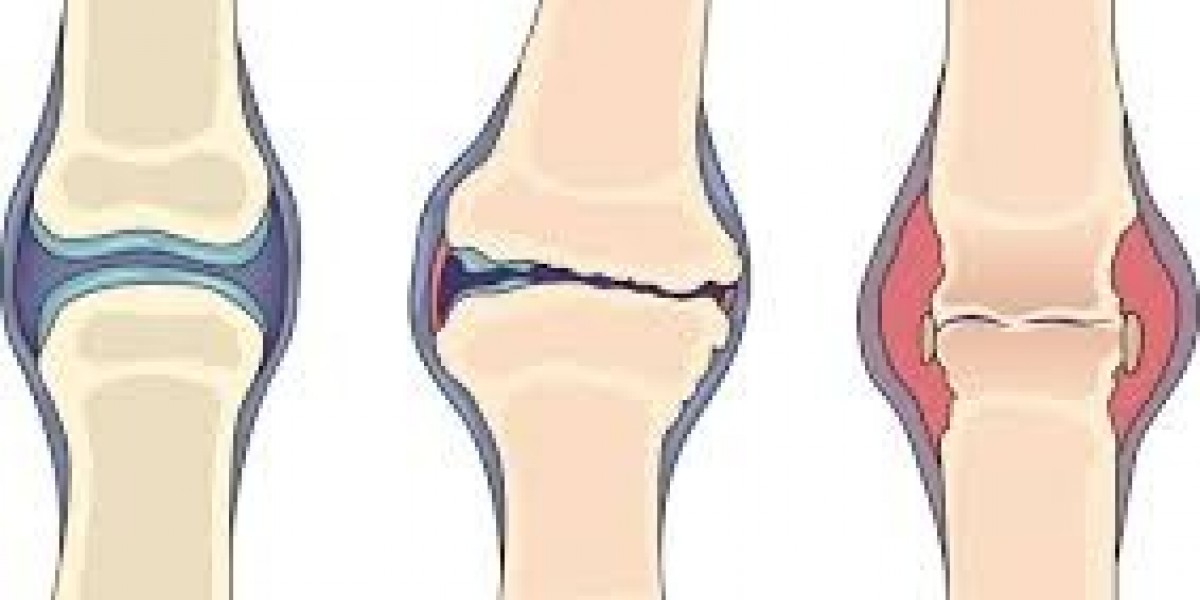
Osteoarthritis is the most common form of arthritis, often referred to as "wear-and-tear" arthritis. It occurs when the cartilage that cushions the ends of the bones in your joints gradually deteriorates. Over time, bones may rub against each other, causing pain, swelling, and reduced mobility.
Causes and Risk Factors:
Aging: Risk increases with age
Joint overuse: Repetitive motion or stress on a joint
Obesity: Extra weight adds pressure to weight-bearing joints
Injuries: Past joint injuries may increase risk
Genetics: Family history may play a role
Symptoms of OA:
Joint pain and stiffness, especially after activity
Reduced range of motion
Swelling in joints
Bone spurs or bony growths
Pain that worsens over time
OA typically affects the knees, hips, hands, and spine. It usually develops slowly and worsens with age.
What is Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)?
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder in which the body's immune system mistakenly attacks the lining of the joints, called the synovium. This causes inflammation that can eventually damage cartilage and bone, leading to joint deformity and disability.
Causes and Risk Factors:
Autoimmune reaction: The immune system attacks healthy tissues
Genetic predisposition
Gender: More common in women
Smoking: Increases risk and severity
Infections: May trigger RA in genetically susceptible individuals
Symptoms of RA:
Swollen, tender, and warm joints
Morning stiffness lasting more than 30 minutes
Fatigue, fever, and weight loss
Symmetrical symptoms (affects both sides of the body equally)
Joint deformity over time
RA commonly starts in smaller joints (like fingers and toes) and may progress to larger joints like knees, ankles, and shoulders. Unlike OA, RA can also affect other systems, including the skin, eyes, lungs, and heart.
Key Differences Between OA and RA
| Feature | Osteoarthritis (OA) | Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) |
|---|---|---|
| Cause | Wear and tear of cartilage | Autoimmune inflammation |
| Onset | Gradual, over years | Can be sudden or gradual |
| Age Group | Usually 50+ | Often 30–60 years |
| Affected Joints | Common in weight-bearing joints | Starts in smaller joints, symmetrical |
| Inflammation | Mild | Prominent and severe |
| Systemic Effects | No | Yes, can affect entire body |
Treatment and Management
There is no cure for either OA or RA, but treatments can manage symptoms and improve function.
Osteoarthritis Treatment:
Pain relievers (acetaminophen, NSAIDs)
Physical therapy
Weight loss
Joint injections
Surgery (e.g., joint replacement)
Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment:
Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs)
Biologic agents
Corticosteroids
Anti-inflammatory medications
Regular monitoring by a rheumatologist
Both conditions benefit greatly from regular exercise, healthy diet, joint protection, and lifestyle modifications.
Conclusion
Osteoarthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis may share joint pain as a common symptom, but they are very different diseases with distinct causes and treatments. While OA is primarily due to physical wear on the joints, RA is an autoimmune condition that requires specialized care. Early diagnosis and appropriate management can help control symptoms, reduce joint damage, and improve quality of life for those living with either condition. If you're experiencing joint pain or stiffness, consult a healthcare provider to determine the cause and get the right treatment plan.